
Most people have an instinctive understanding of what a financial loss is; anytime you receive less for something than what you spent to acquire it, you have sustained a loss, explains AccountingCoach.com. However, it is important not to just recognize that a loss has occurred, but to be able to classify it and report it for financial reporting and tax purposes. They may be the result of a sale of an asset below its carrying amount, from a lawsuit, or a write-down of an asset. Revenue minus cost of goods sold, excluding other expenses such as operating costs and taxes. Revenue reflects how much a company has made through sales while profit is the amount that is made net of expenses, such as salaries, overhead, and production costs.
Uses of the P&L Statement
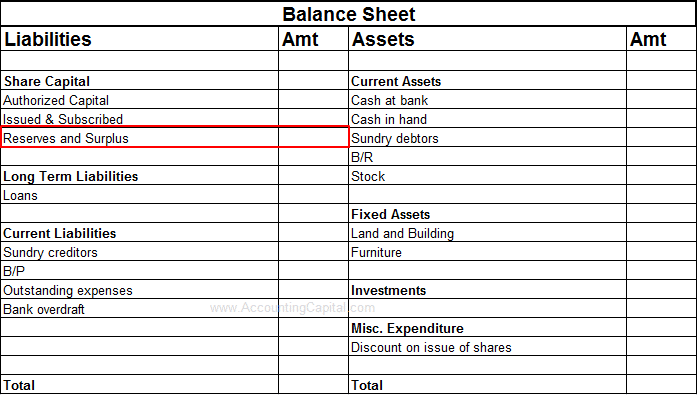
The balance sheet is typically presented as of the last day of the company’s fiscal year. Investors use the balance sheet to understand the financial strength of the company, comparing the amount and quality of its assets against its liabilities. Impairment losses are shown both on the income statement and the balance sheet. An impairment loss is simultaneously recorded as an expense on the income statement and reduces the value of the impaired asset on the balance sheet.
Revenues and Expenses
In case of prevailing losses, the valuation might dwindle as the anticipation of returns on an investment decrease. This scenario could result in an outflow of investors leading to liquidity problems. Losses adversely affect the stock prices, and the shrinking of market capitalization might even instigate a vicious cycle of devaluation. Several financial ratios and metrics take account of revenues and expenses, such as the frequently used EBITDA metric, which is earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization. In other words, it is revenues less expenses related to the production of goods sold.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
For example, property insurance protects against losses to physical assets like buildings and equipment, while liability insurance covers legal claims against the company. Business interruption insurance, on the other hand, compensates for lost income during periods when the company cannot operate normally due to covered events like natural disasters. Publicly traded companies are required to prepare P&L statements and must file their financial statements with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) so that they can be scrutinized by investors, analysts, and regulators.
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
It is important to compare the value of the asset to the fair market value to help determine the loss. Any write-off due to an impairment loss can have adverse effects on a company’s balance sheet and its resulting financial ratios. It is, therefore, important for a company to test its assets for impairment periodically. The value of fixed assets such as machinery and equipment depreciates over time.
Can a company with positive revenues still have a net loss?
Additionally, businesses should regularly review and adjust their coverage to reflect changes in their operations and risk profile. The amount of profit remaining after all expenses and losses have been subtracted from total revenues. Costs incurred to generate revenue, often related to core business operations. When profits fall below the level of expenses and cost of goods sold (COGS) in a given time, a net loss results.
- Appropriate financial planning and risk management strategies can act as valuable safeguards against the adverse impacts of uncertainty.
- Losses represent the excess of expenses over revenues within a specific accounting period.
- This might cause severe reputational damage and impede trust building among stakeholders, customers, and the community-at-large.
- For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online.
Investors and analysts use financial statements to assess the financial health of a company and its growth potential. An operating loss arises when a company’s operating expenses exceed its gross income. In simpler terms, it happens when the revenues from the company’s core business operations are not enough to cover routine operating costs, such as payroll, rent, utilities, and equipment costs. Operating loss reflects operational inefficiencies and might be indicative of problems with a company’s core business model or market conditions in its industry. Operating loss doesn’t take into account taxes or interest on loans, as these are considered to be outside the realm of a company’s typical business operations.
Moreover, businesses must navigate through complex reporting requirements and utilize tools like insurance to mitigate potential risks. The generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) define an asset as impaired when its fair value is lower than its book value. To check an asset for impairment, the total profit, cash flow, or other benefit expected to be generated by the asset is compared with its current book value.
The market position of a company, which shapes the industry dynamics, is tremendously swayed by its financial health. Persistent financial losses can bear negative implications on a company’s reputation, causing potential and existing customers to question its ability to deliver satisfactory services or products. A history of escalating losses can repel stakeholders, including suppliers and creditors, the balance sheet creating challenges in business operations. Loss is the excess of expenses over revenues for a specific period, indicating that a company has spent more than it has earned. It is reported on the income statement and negatively impacts the company’s financial health. A company’s gains and losses, which measure the financial results of non-primary operations, are reported in the income statement.
One of the direct repercussions of financial losses is the decrease in stock value. This increases the supply of the shares on the market, which can lead to a fall in share price. For instance, a company causing a large-scale product recall due to manufacturing defects can lead to huge financial losses. Alternatively, a decision to expand operations into foreign markets without thorough research could also result in losses if the business cannot meet the unique demands of those specific markets. Losses also have tax implications, as they can often be carried forward or backward to offset taxable income in other years, a process known as tax loss carryover.
However, the term negative profit is used colloquially to describe a net loss. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site. All of our content is based on objective analysis, and the opinions are our own. Profitability ratios, derived from the P&L statement, help gauge the efficiency of operations.
Leave A Comment